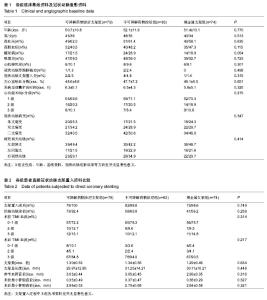
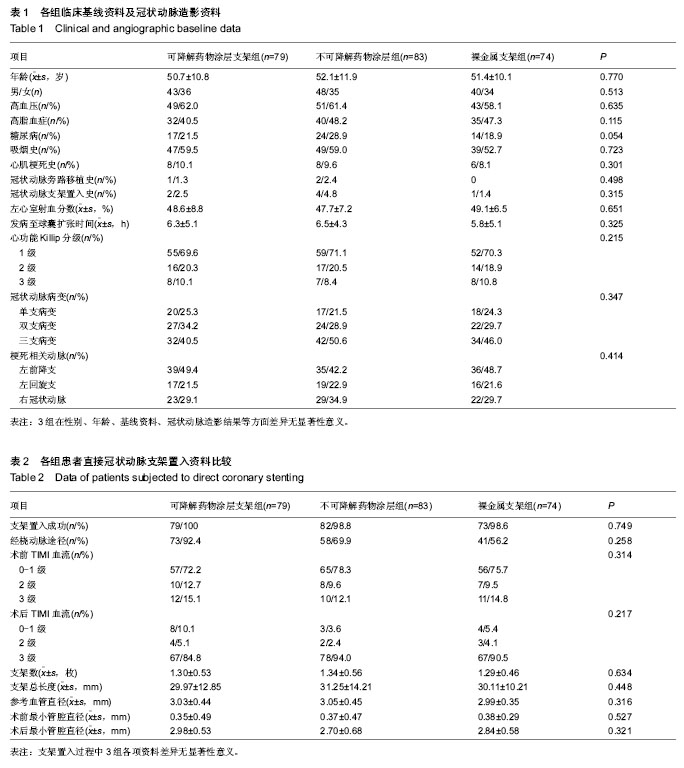
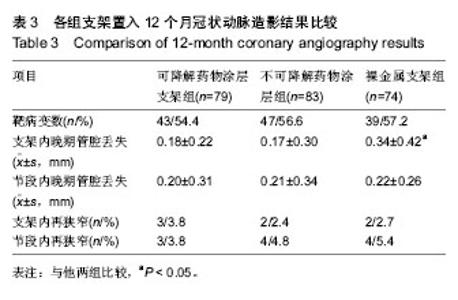
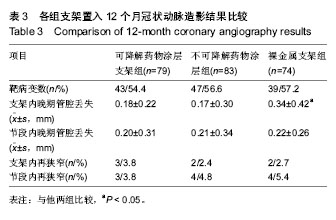
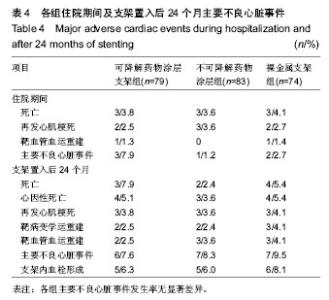
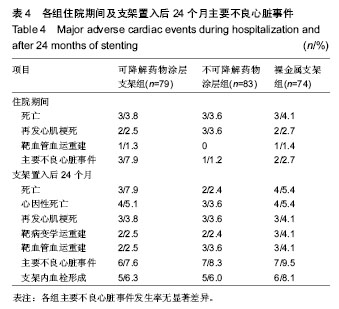
| [1] 张文利,黄定.PCI后冠状动脉再狭窄机制及防治研究进展[J].中国循证心血管医学杂志,2011,3(2):125-128.
[2] 肖越勇,张金山,崔福斋,等.新型生物可降高分子支架[J].中国医疗器械信息,2004,10(2):12-14.
[3] Sun LX,Zhang J. Biodegradable Polymer DES Versus Durable Polymer Everolimus-eluting Stents for Patients Undergoing PCI: A Meta-analysis. Heart Lung Circ. 2014; 23(6): 496-502.
[4] Uurto I,Juuti H,Parkkinen J,et al.Biodegradable selfexpanding polyL/Dlactic acid vascular stent: a pilot study in canine and porcine iliac arteries. Endovasc Ther. 2004;11(6):712-718.
[5] de Waha A,King LA,Stefanini GG,et al.Long-term outcomes of biodegradable versus durable polymer drug-eluting stents in patients with acute ST-segment elevation myocardial infarction: a pooled analysis of individual patient data from three randomised trials.EuroIntervention.2014.pii: 20130419-04. [Epub ahead of print]
[6] Schurtz G,Delhaye C,Hurt C,et al.Biodegradable polymer Biolimus-eluting stent (Nobori®) for the treatment of coronary artery lesions: review of concept and clinical results.Med Devices (Auckl).2014;7:35-43.
[7] Li Q,Tong Z,Wang L,et al.Efficacy and safety of a biodegradable polymer sirolimus-eluting stent in primary percutaneous coronary intervention: a randomized controlled trial. Arch Med Sci.2013;9(6):1040-1048.
[8] Kang SH,Park KW,Kang DY,et al.Biodegradable-polymer drug-eluting stents vs. bare metal stents vs. durable-polymer drug-eluting stents: a systematic review and Bayesian approach network meta-analysis.Eur Heart J. 2014;35(17): 1147-1158.
[9] 张立新,张海滨,高国旺,等.国产雷帕霉素药物洗脱支架在老年急性心肌梗死患者急诊冠状动脉介入治疗中的应用[J].中国心血管病研究杂志,2006,4(6):426-428.
[10] 卢长青,邱春光,宋文翔,等.冠脉内置入药物涂层支架与金属裸支架对血浆C反应蛋白水平影响的对比观察[J].河南医学研究, 2007,16(4):311-313.
[11] Lam MK,Sen H,Tandjung K,et al.Comparison of 3 biodegradable polymer and durable polymer-based drug-eluting stents in all-comers (BIO-RESORT): rationale and study design of the randomized TWENTE III multicenter trial.Am Heart J.2014;167(4):445-451.
[12] Zhang L,Li Y,Jing QM,et al.Dual antiplatelet therapy over 6 months increases the risk of bleeding after biodegradable polymer-coated sirolimus eluting stents implantation: insights from the CREATE study.J Interv Cardiol.2014;27(2):119-126.
[13] 侯云,丁世芳,王慧洁,等.冠状动脉支架置入24 h血清内脏脂肪素变化[J].中国组织工程研究,2014,18(16):2619-2624.
[14] 王禹,盖鲁粤,沈洪,等.国产氯吡格雷在急性心肌梗死急诊冠脉介入治疗过程中的有效性及对血小板聚集功能的影响[J].中国急救医学,2006,26(7):510-513.
[15] 杨玉恒,孙中华,米杰,等.国产与进口氯吡格雷对冠状动脉支架置入后影响的等效性比较:1798例总结[J].中国组织工程研究, 2013, 17(47):8175-8181.
[16] 王磊,刘福全,岳振东,等.TIPS术后支架再狭窄或闭塞的介入治疗[J].首都医科大学学报,2014,35(1):136-139.
[17] Chen MC,Tsai HW,Chang Y,et al.Rapidly self-expandable polymeric stents with a shape-memory property. Biomacromolecules.2007;8(9):2774-2780.
[18] Zhang Y,Tian N,Dong S,et al.Impact of biodegradable versus durable polymer drug-eluting stents on clinical outcomes in patients with coronary artery disease: a meta-analysis of 15 randomized trials. Chin Med J (Engl). 2014;127(11): 2159-2166.
[19] Räber L,Kelbæk H,Taniwaki M,et al.Biolimus-Eluting Stents With Biodegradable Polymer Versus Bare-Metal Stents in Acute Myocardial Infarction: Two-Year Clinical Results of the COMFORTABLE AMI Trial.Circ Cardiovasc Interv. 2014;7(3): 355-364.
[20] Wang Y,Dong P,Li L,et al.Biodegradable Polymer Drug- Eluting Stents Versus Second-Generation Drug-Eluting Stents for Patients With Coronary Artery Disease: An Update Meta- Analysis.Cardiovasc Drugs Ther.2014.[Epub ahead of print]
[21] Natsuaki M,Kozuma K,Morimoto T,et al.Two-year outcome of a randomized trial comparing second-generation drug-eluting stents using biodegradable or durable polymer. JAMA. 2014; 311(20):2125-2127.
[22] Tada T, Kastrati A,Byrne RA,et al.Randomized comparison of biolimus-eluting stents with biodegradable polymer versus everolimus-eluting stents with permanent polymer coatings assessed by optical coherence tomography.Int J Cardiovasc Imaging. 2014;30(3):495-504.
[23] Martin D,Boyle F.Finite element analysis of balloon-expandable coronary stent deployment: influence of angioplasty balloon configuration. Int J Numer Method Biomed Eng.2013;29(11):1161-1175.
[24] Boyle CJ,Lennon AB,Early M,et al.Computational simulation methodologies for mechanobiological modelling: a cell-centred approach to neointima development in stents. Philos Trans A Math Phys Eng Sci. 2010;368(1921): 2919-2935.
[25] Moses JW,Leon MB,Popma JJ,et al.Sirolimus-eluting stents versus standard stents in patients with stenosis in a native coronary artery.N Engl J Med. 2003;349(14):1315-1323.
[26] Zhang J.Stent thrombosis in patients with coronary artery disease treated with biodegradable polymer drug-eluting stents. Int Heart J.2014;55(3):213-218.
[27] Pfisterer M,Kaiser C.Drug-eluting stents with biodegradable polymers: are enough data in for a final assessment? Eur Heart J. 2014;35(17):1098-1100.
[28] Zhang YJ,Ye F,Iqbal J,et al.NOBORI™ biodegradable- polymer biolimus-eluting stent versus durable-polymer drug-eluting stents: A meta-analysis.Int J Cardiol. 2014;174(1): 151-153.
[29] 王勇,曲华,齐国先,等.钴合金裸支架与雷帕霉素药物涂层支架在冠心病患者应用中的对比研究[J].中国医科大学学报, 2008, 37(3):374-375.
[30] 李超民,李慧,拓步雄,等.药物涂层支架与金属裸支架治疗ST段抬高型心肌梗死的临床价值比较[J].现代生物医学进展, 2014, 2(13):302-304. |